Ultimate Guide to Apply Field Testing for Mobile Application
Field Testing and Its Importance
Field testing is a critical step in the last phase of mobile testing. After all regression tests pass, testers would go into the real environment to verify an application’s usability and behavior. The purpose of field testing is to determine how an application works before releasing it to end-users. Therefore, teams test to see how end-users use the application beyond the initial frequent use, in a real-world scenario. Testing is carried out using mobile networks only.
Importance of Field testing
- It helps to improve the application success by providing trend-based recommendations for a positive outturn.
- It points out issues that might be frequently reported after product launch.
Limitations of Field testing
- Field testing can be time-consuming because it requires a large resource allocation: dedicated QA teams taking devices out into real-world scenarios.
- Purchasing a wide range of devices (with different models or versions) for adequate field testing will cost thousands of dollars annually.
Differences between In-house testing and Field testing
Mobile testing is classified into two categories, in-house/lab testing and field testing.
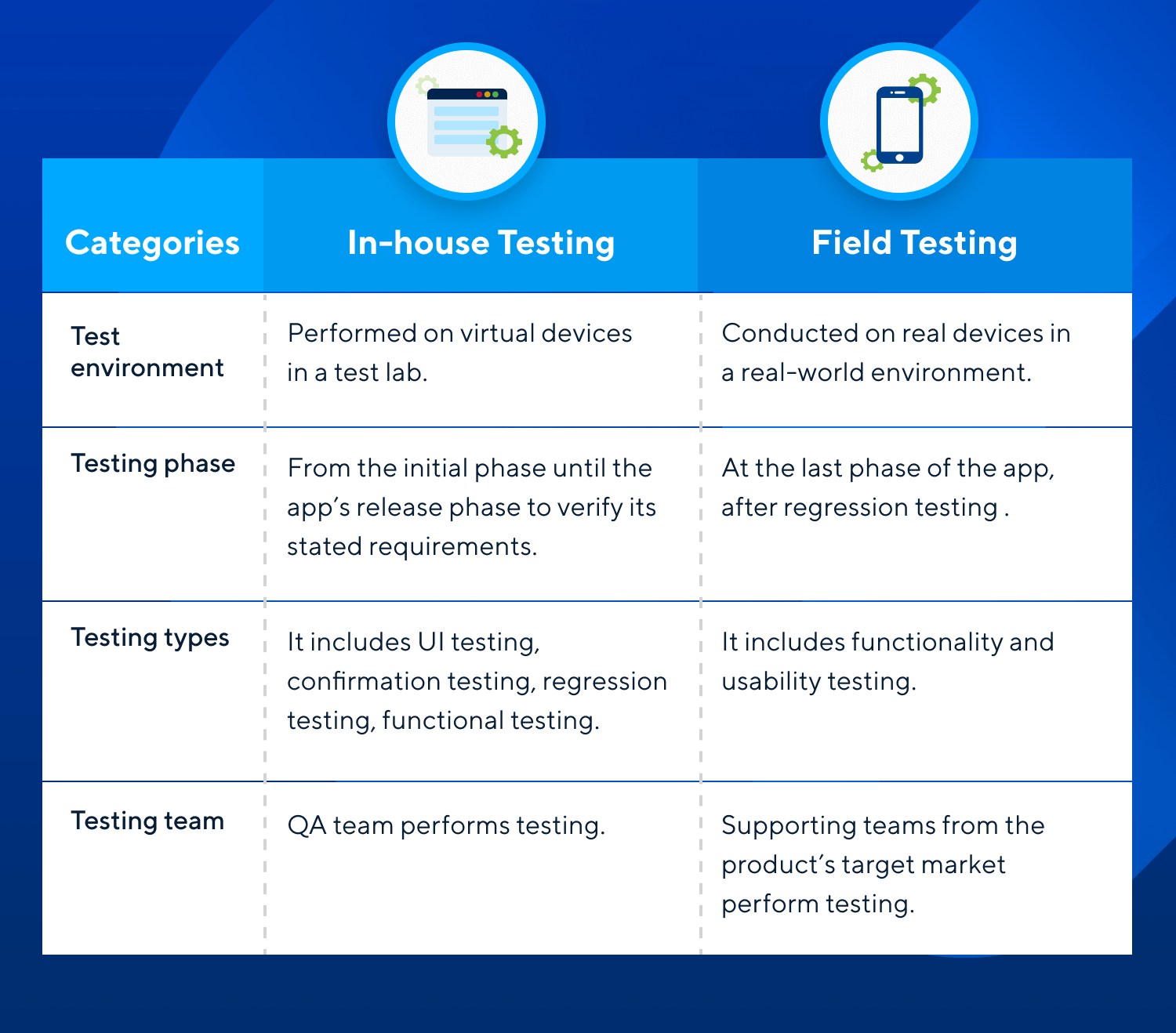
In spite of the differences between in-house testing and field testing, both activities are essential in each software application development. They help stakeholders better understand the target customer and how they experience the product, by having all of the tests moving from being quality-focused to being experience-focused.
When Should the Team Perform Field Testing?

Testers should only perform field testing after thorough in-house testing for the app’s functionality has been done. The essential element for a field test are as follows:
- A routinary testing procedure
Field testing for a mobile application should be repeated regularly, just as regression and automation testing is. Doing this helps to procure a sense of stability for the app.
- The first release of the application
Field testing allows the testing team to thoroughly analyze the app like an end-user in a real environment. It helps the testers examine the application’s features and performance before its availability for other Play Store/App Store users.
- When an application is designed for a specific OS
Field testing is also necessary when a new release for a native application is launched (even if no changes were made to the app features). This results from the native app which uses the mobile device’s features and operating system (Android or IOS).
- A new OS is launched or updated
When a new OS is launched or updated, testers need to verify the app using the right software testing tool. Testers carry out field testing to ensure that the app is functioning at optimal in its performance, stability, and compatibility against the new environment.
- Release of a new application or a change in its features
It is essential to do a field test when a new app is updated, or existing features are updated. This helps testers to verify that the performance of such apps or components is not altered negatively.
Some examples of test that can be verified in field test
- Testing of a mobile app on different phone models or network types in a crowded area (market or cinema) while on the bus, driving, or walking on the road as an end-user. This will help you understand any major issues users might face while sending or fetching data through the app.
- Another example is testing a travel app used to book a train, try and log in as an end-user (do this in different locations, different phone models, and network mode. This is necessary to verify the application’s end-to-end flow, from the minutes spent logging in to booking a seat. You can also access the app’s review feature to write feedback and check if the input is submitted successfully and appear on the review list.
6 Best Practices for Field Testing
- Carry out a field test only after regression tests are done for your application, and there is no issue in its functionality.
- Before performing a field test for an app, create some test cases depending on its purpose and the users.
- Discuss the field test with your development team to see if anything can be added to the test cases you have already created.
- Keep a record chart with all details of test cases, how it will be executed, and each execution’s results. This will allow you to see areas that require improvement for future releases.
- Test your application on two devices with the same OS (a budget smartphone and a flagship device. This will allow for better analysis of the performance and any defect found on any of the devices.
- Create a roadmap of the testing procedure or techniques to follow on the field. For example, the various places to carry out tests, the member executing, the places where it was tested and defects reported. This roadmap can also be used for evaluating future releases.
Conclusion
A field test is a significant part of any mobile application testing cycle. An application can only be verified as stable and fast when it undergoes this journey. Field testing allows testers to take their devices into the real world and explore its applications as an end-user would.
Mobile application field testing can also cost testers their time and effort if not prepared properly. Follow the best practices in this article to carry out your field testing to achieve your desired outcome.
Read more: Simulators vs Emulators vs Real Devices | Mobile Testing Differences